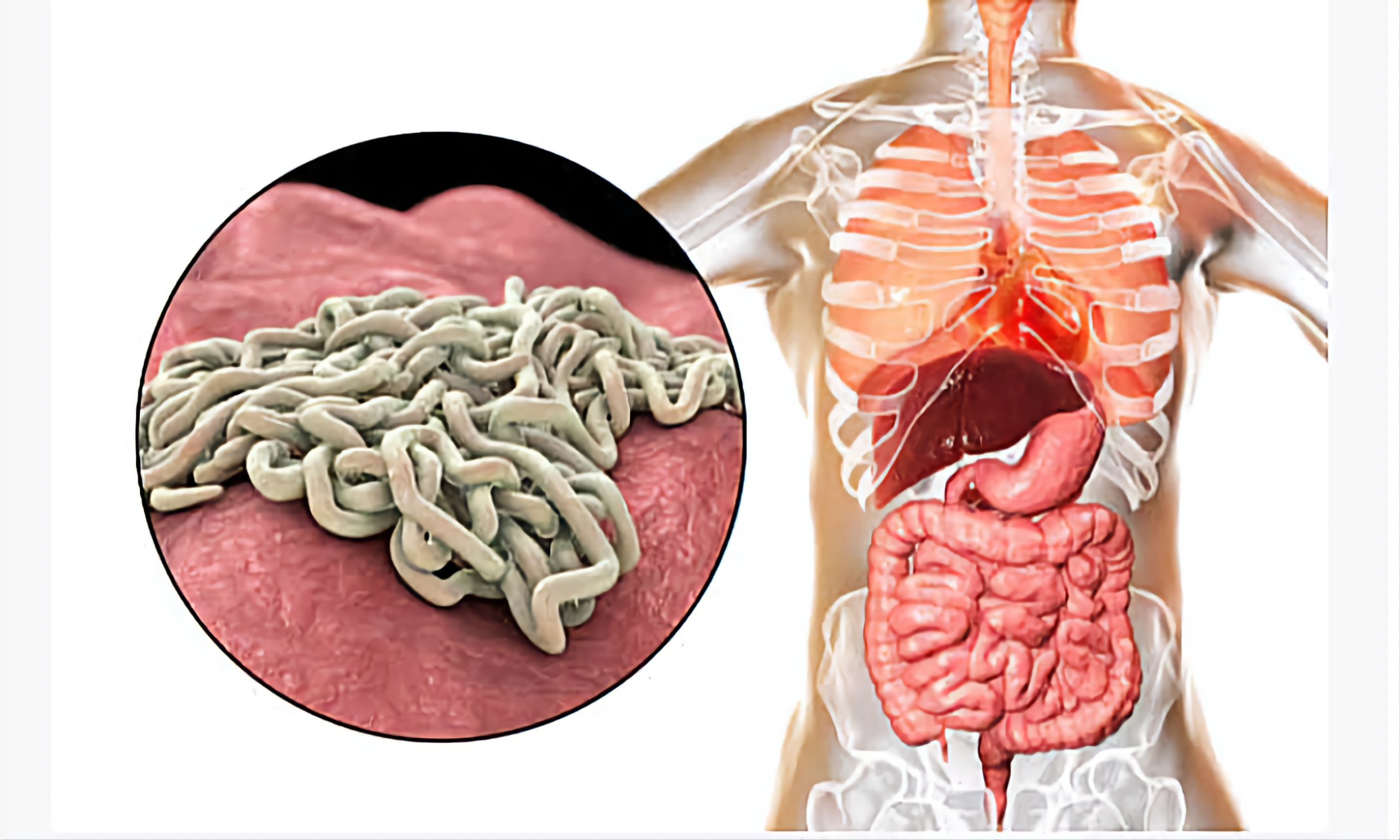
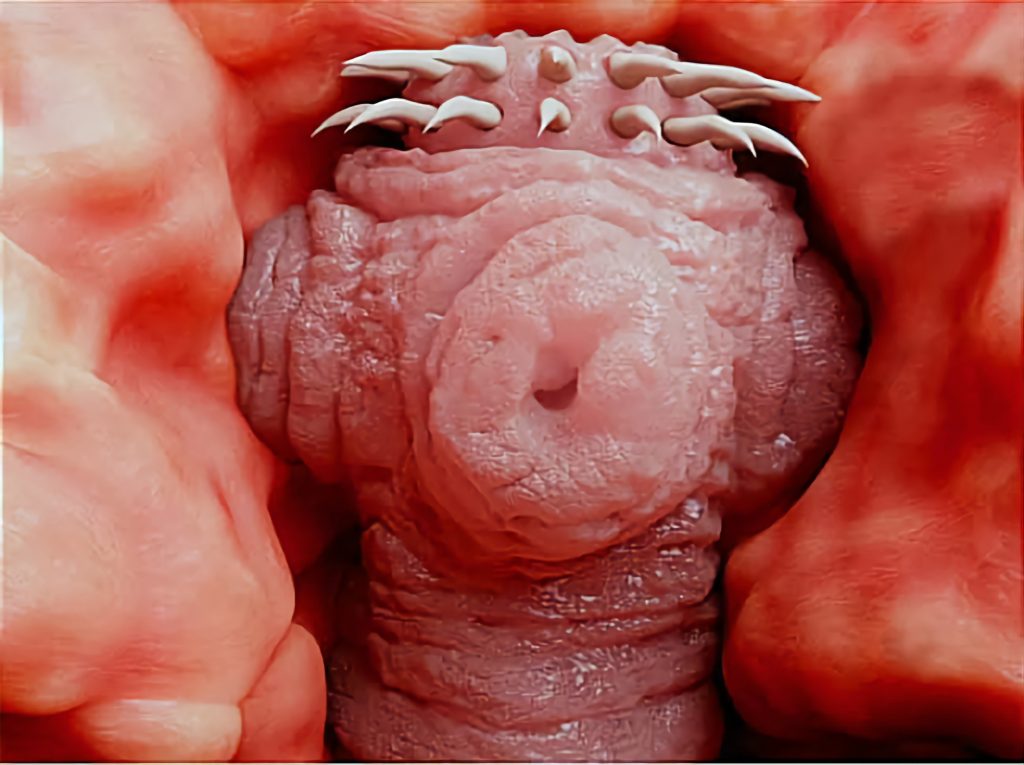
Some intestinal parasites, like tapeworms, can migrate to the brain and nervous system, causing, seizures, headaches and other neurological symptoms.
Some like roundworms, can migrate to the liver and lungs causing damage and inflammation.
Parasites can also release toxins that are absorbed into the bloodstream and carried to the liver, causing damage and inflammation.
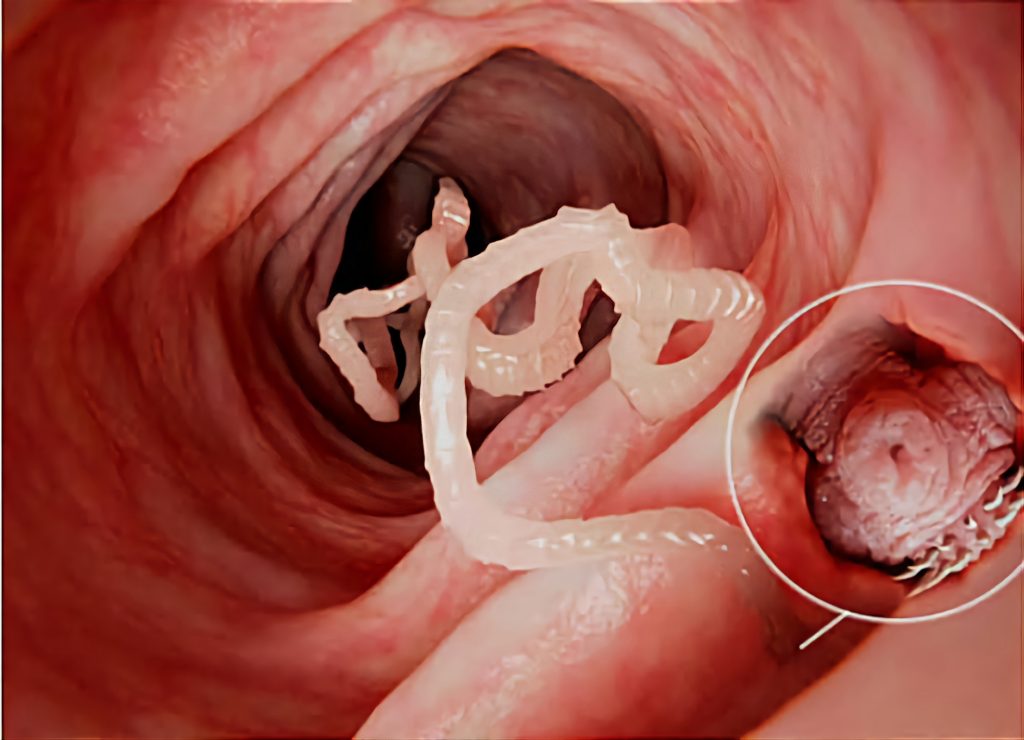
Intestinal parasites can be transmitted through the following routes:
Contaminated Food and Water
✓ Consuming undercooked or raw meat, poultry, or fish.
✓ Eating unwashed or contaminated fruits and vegetables.
✓ Drinking contaminated water or ice.
✓ Consuming unpasteurized dairy products or juices.
Poor Hygiene and Sanitation
✓ Not washing hands properly after using the toilet or before handling food.
✓ Not disposing of human waste properly.
✓ Living in areas with poor sanitation and hygiene.
Direct Contact
✓ Touching contaminated feces or vomit.
✓ Sharing personal items, such as towels or utensils, with an infected person.
Vectors and Animals
✓ Being bitten by an infected insect, such as a mosquito or fly.
✓ Coming into contact with contaminated feces of animals, such as dogs or cats.
✓ Handling contaminated soil or feces while gardening or playing with pets.